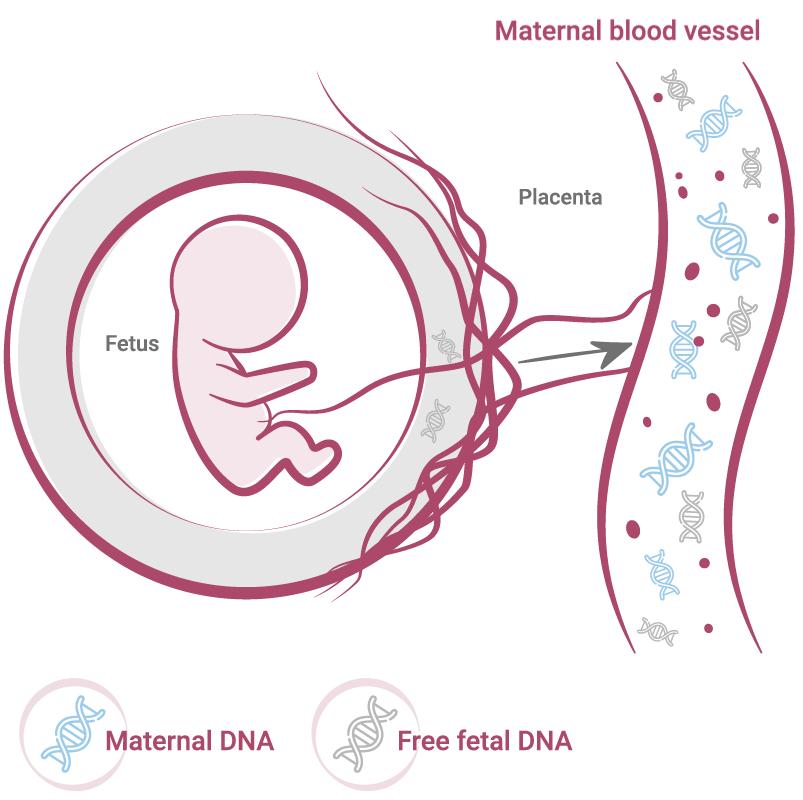
Principle of the Test
During pregnancy, free fetal DNA enters the mother's bloodstream, creating a mixture of maternal and fetal DNA fragments circulating in the maternal circulation. The method of massive parallel sequencing allows us to assign each of the millions of DNA fragments in the mother's plasma to the chromosome it originates from, thus identifying an excess or deficiency of DNA from a specific chromosome in the fetus.
In case of a positive result, the finding must be confirmed by invasive fetal examination – genetic testing of fetal tissue obtained through chorionic villus sampling (CVS) or amniocentesis (AMC).